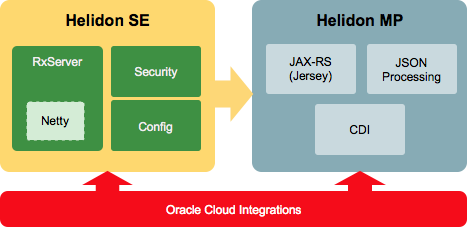
Oracle MySQL Cloud Service is a single MySQL server having full access to the features and its operations.
Steps in creating an instance of Oracle MySQL Cloud Service
1. Login to your cloud account.
2. From Action Menu, select Open Service Console
3. Click Create Service
4. Input the Instance Name, Region and Availability Domain
5. Next page, input the compute shape, ssh key, cloud storage container, username, password, storage size, administrator username, password, database schema name and port.
6. Once you confirm, you could see the mysql instance running in your dashboard.
7. With your ssh keys and inputed connection string, you can either ssh or connect database from your application.
Appendix